Table Of Content

This should be the goal whenever possible because then you have fewer parameters to estimate, and a simpler structure to represent the underlying scientific process. Note that this is not a new level to our Distraction IV, but a whole new IV. In one condition, people will get $5 for every difference they find (so they could leave the study with lots of money if they find lots of differences).
Central composite design (CCD) approach to develop HPLC method for caffeine: Application to coffee samples ... - ScienceDirect.com
Central composite design (CCD) approach to develop HPLC method for caffeine: Application to coffee samples ....
Posted: Tue, 21 Nov 2023 18:34:14 GMT [source]
1: Factorial Designs
The pretend experiment will measure hangriness (we ask people how hangry they are on a scale from 1-10, with 10 being most hangry, and 0 being not hangry at all). The first independent variable will be time since last meal (1 hour vs. 5 hours), and the second independent variable will be how tired someone is (not tired vs very tired). I imagine the data could look something the following bar graph.
Graphical Approaches to Finding a Model
Suppose that you are looking to study the effects of hours slept (A), hours spent with significant other (B), and hours spent studying (C) on a students exam scores. You are given the following table that relates the combination of these factors and the students scores over the course of a semester. Use the Yates method in order to determine the effect each variable on the students performance in the course. The Pareto charts show which factors have statistically significant effects on the responses. As seen in the above plots, RPM has significant effects for both responses and pressure has a statistically significant effect on wt% methanol in biodiesel. Neither flow rate or ratio have statistically significant effects on either response.
The Effects Model vs. the Means Model
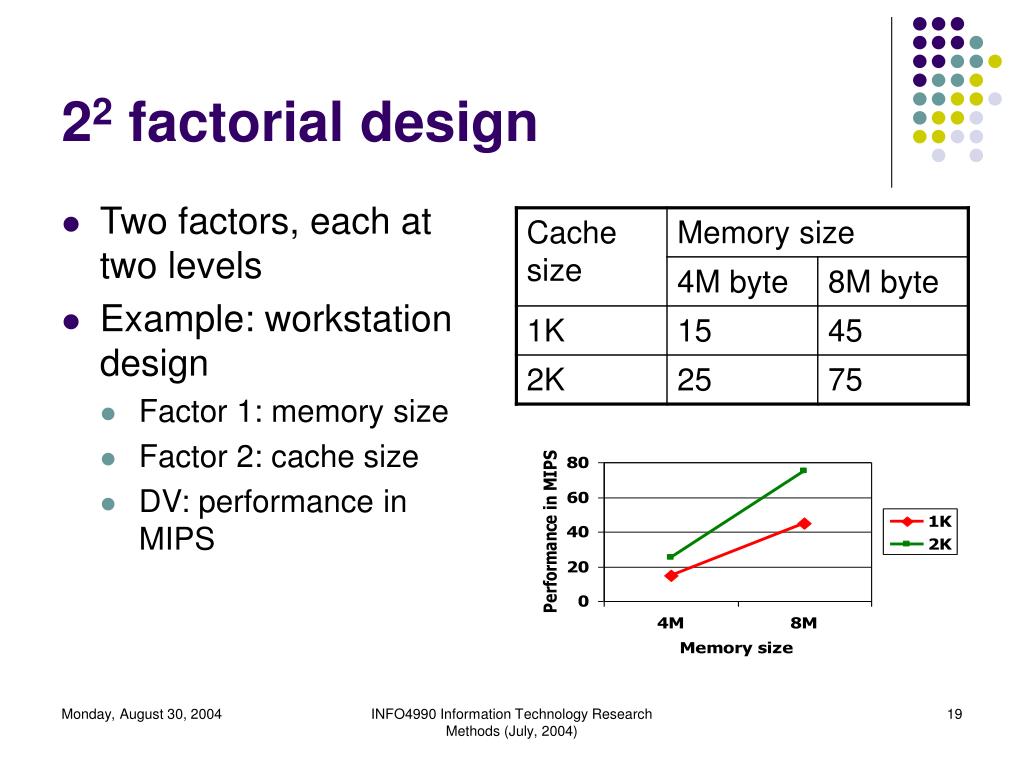
For example, people are either low in self-esteem or high in self-esteem; they cannot be tested in both of these conditions. If one of the independent variables had a third level (e.g., using a handheld cell phone, using a hands-free cell phone, and not using a cell phone), then it would be a 3 × 2 factorial design, and there would be six distinct conditions. Notice that the number of possible conditions is the product of the numbers of levels. A 2 × 2 factorial design has four conditions, a 3 × 2 factorial design has six conditions, a 4 × 5 factorial design would have 20 conditions, and so on.
Selecting the Right Factors and Components in a Factorial Design: Design and Clinical Considerations
In the other condition, people will get no money, but they will still have find differences (comparison control condition). The additional complication is the fact that more than one trial/replication is required for accuracy, so this requires adding up each sub-effect (e.g adding up the three trials of a1b1). By adding up the coefficient effects with the sub-effects (multiply coefficient with sub-effect), a total factorial effect can be found. This value will determine if the factor has a significant effect on the outcome. For larger numbers, the factor can be considered extremely important and for smaller numbers, the factor can be considered less important.
In other words, we want to find out what other IVs might affect the size of the distraction effect (make it bigger or smaller, or even flip around!). Replicates are repeats of each trial that help determine the reproducibility of the design, thus increasing the number of trials and accuracy of the DOE. To add replicates, click the "Replicate design" radio button in the "Modify Design" menu. Copyright © 2024 Elsevier B.V., its licensors, and contributors.
3.2. Main effects¶
In the 2 × 3 example, for instance, the pattern of the A column follows the pattern of the levels of factor A, indicated by the first component of each cell. A contrast in cell means is a linear combination of cell means in which the coefficients sum to 0. Contrasts are of interest in themselves, and are the building blocks by which main effects and interactions are defined. The researchers then decided to look at three levels of sleep (4 hours, 6 hours, and 8 hours) and only two levels of caffeine consumption (2 cups versus no coffee). By doing this, psychologists can see if changing the independent variable results in some type of change in the dependent variable. The effect of one independent variable can depend on the level of the other in several different ways.
In smoking cessation research a common RCT design is one in which participants are randomly assigned to either an active pharmacotherapy or to placebo, with both groups also receiving the same counseling intervention. There are a few other methods, such as fractional factorial designs, to reduce this, but they are not always statistically valid. This lies firmly in the realm of advanced statistics and is a long, complicated and arduous undertaking. Rather than the traditional experiment, the researchers could use a factorial design and co-ordinate the additive trial with different stocking densities, perhaps choosing four groups.
To have a total of 3 trials of each, the user should add 2 replicates in this menu. If 4 replicates are added, there will be a total of 5 trials of each. Typically, if the same experimentation will occur for 3 lab periods, 2 replicates will be added. Once the design has been chosen, the "Factors...", "Options..." and "Results..." buttons become active in the "Create Factorial Designs" option menu. After the number of factors is chosen, click on the "Designs..." option to see the following menu. Onwards, the minus (−) and plus (+) signs will indicate whether the factor is run at a low or high level, respectively.
Another example is a study by Halle Brown and colleagues in which participants were exposed to several words that they were later asked to recall [BKD+99]. Some were negative, health-related words (e.g., tumor, coronary), and others were not health related (e.g., election, geometry). The non-manipulated independent variable was whether participants were high or low in hypochondriasis (excessive concern with ordinary bodily symptoms). Results from this study suggested that participants high in hypochondriasis were better than those low in hypochondriasis at recalling the health-related words, but that they were no better at recalling the non-health-related words.
And, we can test the hypothesis that the interaction effects are all equal to zero. The alternative hypotheses are that at least one of those effects is not equal to zero. Now, we'll take a look at the strategy for deciding whether our model fits, whether the assumptions are satisfied and then decide whether we can go forward with an interaction model or an additive model. When you can eliminate the interactions because they are not significantly different from zero, then you can use the simpler additive model.

No comments:
Post a Comment